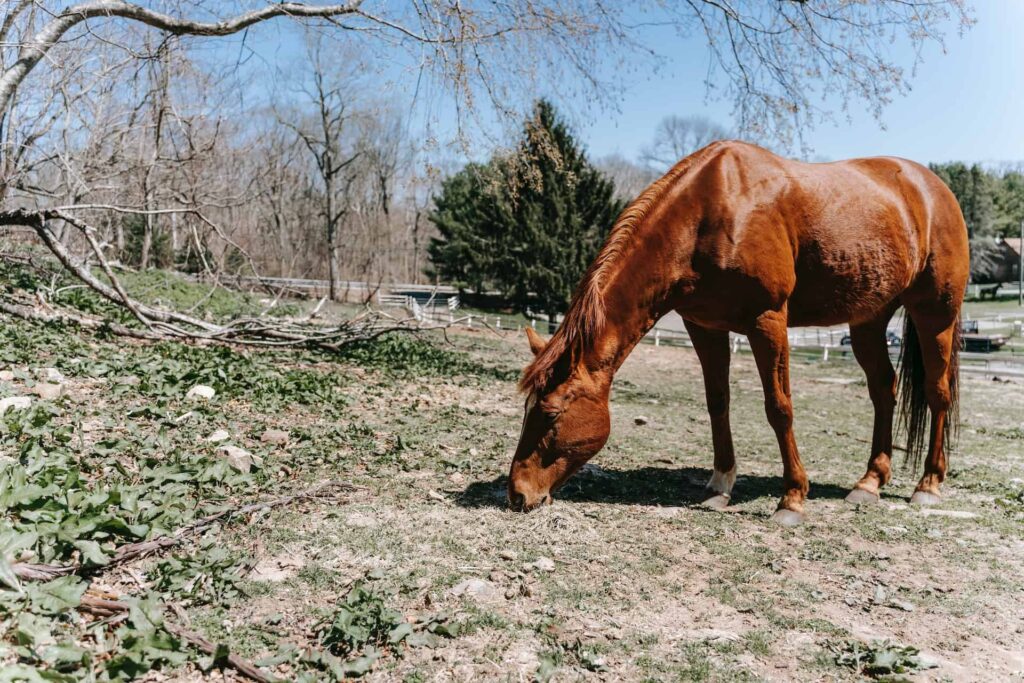
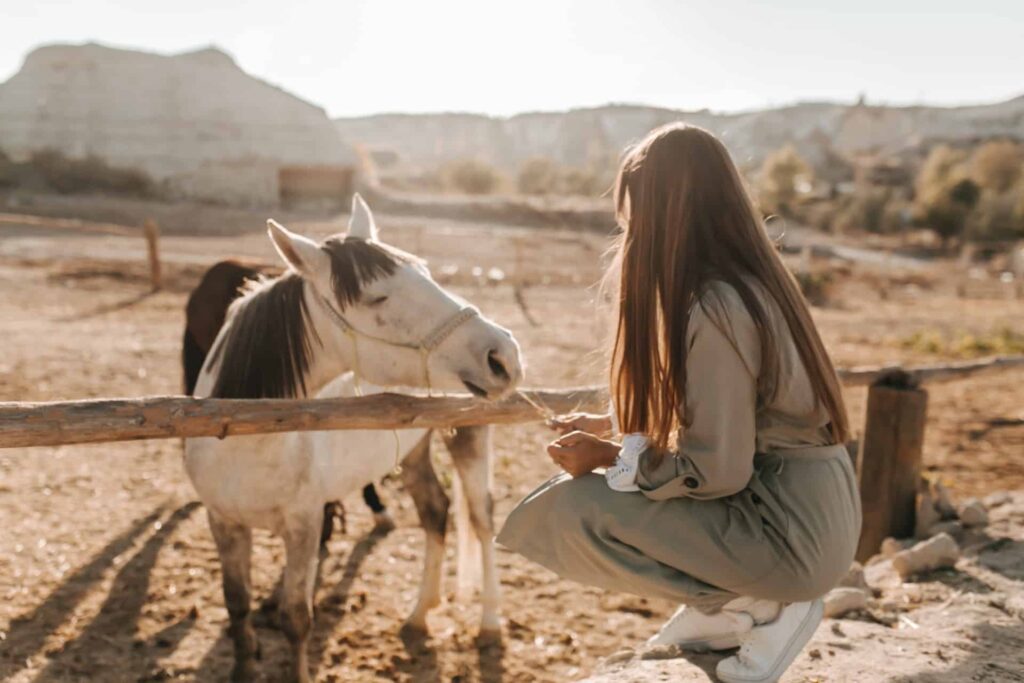
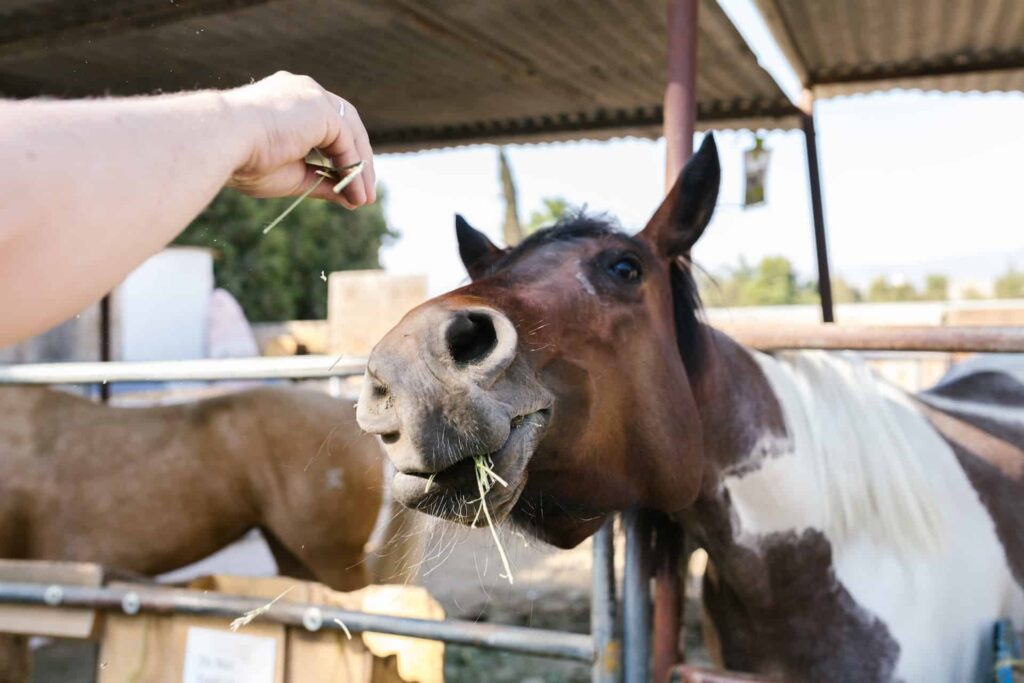
Horses have unique dietary needs and understanding their eating habits is essential to ensure their overall health and well-being. As herbivores, their main source of nutrition comes from plant-based forage, such as hay and grass. In the wild, horses graze for most of the day, allowing their digestive systems to process small amounts of food continuously.
In addition to forage, horses may also require supplementary feeds, such as grains, to meet their nutritional needs, particularly during strenuous activities or if they have specific dietary requirements. Furthermore, a balanced diet geared towards a horse’s age, size, and activity level plays a crucial role in maintaining their overall health.
Key Takeaways
- Horses primarily consume plant-based forage, like hay and grass, as the main component of their diet
- Supplementary feeds may be necessary to ensure nutritional needs are met, depending on the horse’s specific requirements
- A balanced diet based on a horse’s age, size, and activity level is essential for overall health and well-being
Understanding a Horse’s Diet
Horses are herbivores, which means they primarily eat plant-based food. Their diet mainly consists of natural roughage, such as pasture grasses, hay, and forage. Horse owners need to understand the proper nutrition their horse requires to maintain optimal health and body weight.
The nutritional needs of a horse depend on various factors like age, weight, and activity level. To cater to these needs, horses should have a well-rounded diet that provides essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. A horse’s digestive system is designed to process fibrous plants; hence, an adequate amount of forage should be the foundation of their diet.
A common rule of thumb for feeding horses is to provide 1.5% to 2.5% of their body weight in forage each day. For example, a 1000-pound horse would require 15 to 25 pounds of forage daily. However, it’s crucial to adjust the amounts based on the individual horse’s specific needs.
The following table summarizes the essential components of a horse’s diet:
| Component | Importance |
|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | Main energy source, typically provided by forage, grains, and fibrous plants |
| Proteins | Necessary for growth, maintenance, and repair of body tissues |
| Fats | Additional energy source can improve coat condition and overall body condition |
| Vitamins | Required for vital bodily functions, usually found in feed, hay, and supplements |
| Minerals | Important for healthy bones, muscles, and overall well-being, obtained through hay, feed, and water |
Besides these essential nutrients, a continuous supply of clean, fresh water is crucial for maintaining good health in horses. Water helps regulate body temperature, aids in digestion, and supports overall hydration.
Consider the quality of forage, as it directly impacts a horse’s nutritional intake. Good quality hay should have a fresh smell, be free from mold and dust, and have a green color. When choosing feeds for horses, consider feed products specifically designed for equines, as they will cater to their particular nutritional needs.
Understanding a horse’s diet is vital for maintaining their health, body weight, and overall well-being. Regularly evaluate and adjust their diet as needed based on their age, weight, and activity level to ensure they receive proper nutrition.
Fundamentals of Equine Nutrition
Role of Forage
Forage, which includes grasses and hay, is the primary component of a horse’s diet. Horses have evolved to graze for most of the day and their digestive systems are best suited to handle a continuous intake of fibrous plant material. The high fiber content in forage is essential for maintaining proper gut function, and it provides a steady energy source through carbohydrates. Different types of grasses and hay offer varying levels of nutrients, making it essential to select the appropriate forage based on the horse’s nutritional needs.
Importance of Water
Water is a critical component of a horse’s diet. A well-hydrated horse can maintain proper body temperature, digest food more effectively, and support overall health. Horses can consume between 25 and 55 liters of water daily, depending on factors such as activity level, air temperature, and individual needs. Providing free access to clean, fresh water is crucial for every horse.
Essential Nutrients
Horses, like all animals, require a balance of essential nutrients for proper growth, maintenance, and performance. These nutrients include protein, minerals, vitamins, and energy sources such as carbohydrates and fat.
- Protein: Horses need protein to build and repair tissues, including muscles, organs, and skin. The quality and quantity of protein required depends on factors such as age, workload, and reproductive status.
- Minerals: Essential minerals, such as calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium, are crucial for skeletal development, nerve transmission, and various biochemical processes. Horses may require supplementation with minerals if their forage does not provide adequate amounts.
- Vitamins: Horses rely on vitamins for a variety of important functions, including antioxidant defense, cellular maintenance, and metabolism regulation. Most horses obtain adequate vitamins from their forage and sunshine, but some conditions may necessitate supplementation.
Understanding the basic principles of equine nutrition is key to ensuring that horses receive an appropriate diet. By providing an appropriate balance of forage, water, and essential nutrients, horse owners can support the overall health and well-being of their equine partners.

Common Forage and Feed Types
Let’s discuss common forage and feed types for horses. Wwe will cover grasses and hay, grains and concentrates, and vegetables and fruits.
Grasses and Hay
The primary component of a horse’s diet is forage, which includes grasses and hay. Horses graze on pasture grass and consume hay as a common feed source when fresh grass is not available or when stabled.
| Forage Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Pasture Grass | Fresh, natural grasses that horses graze on. |
| Hay | Dried grass, preserved for feeding during periods when pasture grass is unavailable. |
Some common types of hay include alfalfa and haylage, a high-moisture hay made from grasses that have been allowed to wilt before being baled. Both alfalfa and haylage provide essential nutrients for horses. Link to Cambridge Article
Grains and Concentrates
Horses are often fed grains and concentrates to supplement their forage intake, providing additional energy and essential nutrients. Common grains fed to horses include oats, corn, barley, and wheat.
| Grain Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Oats | Nutrient-rich grain, easy to digest. |
| Corn | High in energy, but low in protein and fiber. |
| Barley | Nutrient-dense, often fed after being processed (rolled or crushed). |
| Wheat | Occasionally used in horse feeds, but not as common as other grains. |
Grains should be fed in appropriate amounts, ensuring a balanced diet for the horse. Link to controls of feeding in horses
Vegetables and Fruits
Occasionally, owners may feed horses vegetables and fruits as treats or to supplement their main diet. Some popular choices are carrots, apples, and bananas.
| Produce Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Carrots | Nutritious, high in vitamins and minerals. |
| Apples | Sweet treat, high in fiber. When fed, remove seeds. |
| Bananas | High in potassium, fed with or without the peel. |
It is essential to remember that when feeding fruits and vegetables to horses, they should be given in moderation and as part of a well-balanced diet.
Supplementing the Equine Diet
Horses require a balanced diet to maintain optimal health and performance. While most of their nutritional needs can be met through grazing and the consumption of hay or pasture, there are instances when specific supplements are needed. These include vitamins and minerals supplementation, as well as specialty feed additives.
Vitamins and Mineral Supplements
Horses may not always receive the necessary vitamins and minerals from forage and grains alone, particularly if they have specific health issues. In such cases, owners might choose to provide extra support through supplementation. It is essential, however, to consult a veterinarian or equine nutritionist to determine the right balance of vitamins and minerals that a horse requires.
- Salt: Horses need a salt intake to maintain proper fluid balance and electrolyte levels in their body. Owners can provide a salt lick available for the horse to consume as needed.
- Vitamins: Essential vitamins, such as vitamins A, D, and E, might need supplementation, especially for horses with limited access to fresh pasture.
- Minerals: Minerals like calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium are vital for a horse’s growth, bone health, and muscle function, among other benefits.
Specialty Feed Additives
Aside from basic vitamin and mineral supplements, other specialty feed additives can be useful for certain equine conditions or to improve diet palatability. These may include:
- Molasses: Molasses is a natural sweetener that can be added to the horse’s feed to improve its taste and encourage consumption. It also provides a source of calories and trace minerals.
- Probiotics and Prebiotics: These substances can help support the horse’s gastrointestinal health by promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
- Digestive Enzymes: These additives can aid in the breakdown and absorption of nutrients from the horse’s diet.
It is crucial to monitor a horse’s response to supplementation and adjust the diet as needed. Over-supplementation can be counterproductive and have negative health effects. Always consult with a veterinarian or equine nutritionist when considering supplementation for a horse’s diet.
Feeding Practices and Routines
When it comes to horses, understanding their nutritional needs and feeding practices is essential in maintaining their health and well-being. Different types of horses require varying diets depending on their age, activity level, and living conditions. In general, horses thrive on a diet composed primarily of forage, such as grasses, hay, and alfalfa, with added concentrates when needed.
Age-based Diet Variations
Young horses have different nutritional requirements compared to adult and senior horses. Foals need a higher protein intake to support their rapid growth and development. As they grow older and transition into adolescence, their protein needs will decrease while energy requirements increase to support growth and activity levels.
For adult horses, their diet should focus primarily on providing adequate energy and nutrients to maintain proper body condition and support their daily activities. Similar to young horses, protein intake should be adjusted according to the horse’s work and activity level. It is important to closely monitor the horse’s weight and adjust feeding practices accordingly to prevent health issues such as obesity.
When it comes to senior horses, typically have special nutritional needs due to changes in their metabolism and reduced efficiency in nutrient absorption. They may require a more easily digestible form of forage, as well as additional protein, vitamins, and minerals.
Adapting to Activity Levels
Horse’s diets should be tailored to their activity level. Horses with higher activity levels, such as those involved in competitive sports or heavy work, will require increased caloric intake to maintain their energy and body condition. This can be achieved by adding concentrates, such as grains, pellets, or commercially available horse feeds, to their diet.
For horses with lower activity levels, such as those at rest or used lightly, their caloric needs will be lower. Maintaining these horses on a primarily forage-based diet may be sufficient to meet their nutritional requirements. Overfeeding should be avoided to prevent obesity and related health issues.
Grazing is the most natural way for horses to consume their food and is highly recommended as it allows them to forage for a longer period, promoting a healthy digestive system. In contrast to stabled and confined horses, those who are allowed to graze freely tend to have fewer digestive issues and display less stereotypic behaviors. Monitoring the quality of pasture and the horse’s body condition is crucial for making dietary adjustments when necessary.
For stable or confined horses, it is important to provide an appropriate feeding schedule that mimics their natural grazing behavior. This typically involves offering hay or other forage sources multiple times throughout the day in small quantities. Concise attention should be given to their needs and preferences, ensuring that they are receiving the optimal diet for their age, activity level, and weight.
Health Considerations in Feeding
When it comes to feeding horses, it is important to consider their overall health, as well as specific issues related to weight management and digestive disorders. In this section, we will discuss managing weight and obesity, as well as preventing common digestive disorders in horses.
Managing Weight and Obesity
Equine obesity is a growing concern among horse owners. Obesity can lead to a variety of health issues, such as laminitis and insulin resistance. To maintain a healthy weight, it is crucial to provide a diet that meets the horse’s nutritional needs without exceeding their caloric requirements.
It is essential to regularly monitor the horse’s body condition and adjust their diet as necessary. Feeding appropriate amounts of high-quality forage such as hay or grass should be prioritized as the main source of the horse’s calories. Ensuring that horses have access to free-choice mineral supplements can also help prevent nutritional imbalances. When additional calories are needed, consider using low-energy feeds such as beet pulp or rice bran instead of high-calorie grains.
Preventing Digestive Disorders
A horse’s digestive system is sensitive, and improper feeding practices can lead to disorders like colic, ulcers, and digestive tract inflammation. To support healthy digestion, it is essential to follow proper feeding routines and provide an appropriate diet.
Frequency of Feeding: Horses are designed to eat small meals frequently throughout the day. Avoid feeding large meals to prevent overloading the stomach and digestive system. Instead, provide smaller, more frequent meals that mimic the horse’s natural grazing habits.
Forage Quality: High-quality forage plays a crucial role in maintaining digestive health. Adequate forage intake can help prevent problems like gastric ulcers and colic. Ensure that the forage provided is clean, mold-free, and appropriate for the horse’s nutritional requirements.
Balancing Nutrients: A balanced diet is important for optimal digestive health. Feeding a diet that meets the horse’s needs for energy, protein, vitamins, and minerals is essential to support healthy digestion and overall well-being. Using a nutritionally balanced commercial feed that is suitable for the horse’s age, weight, and workload can simplify this process.
Preventing Rapid Diet Changes: Sudden changes in a horse’s diet can disrupt the delicate balance of bacteria in their digestive tract, resulting in colic or other digestive issues. Gradually introduce new feeds and forage for 7 to 10 days to allow the horse’s digestive system to adapt to the changes.
By keeping these factors in mind, horse owners can make more informed decisions about feeding practices that support their horse’s health and well-being.
Unsafe Foods for Horses
Horses have specific dietary requirements and some human foods can be dangerous for them. It is essential to provide a safe and nutritious diet for optimum health. This section highlights some unsafe foods that horses should avoid.
Chocolate is harmful to horses due to the presence of theobromine, a compound found in cocoa products. Theobromine can cause increased heart rate, seizures, and even death in horses. Thus, it is crucial to keep chocolate away from their reach.
Avocados contain a toxin called persin, which can cause respiratory distress and heart failure in horses. Avoid offering avocado in any form, including leaves and fruit, to prevent severe health complications.
The nightshade family of plants, including tomatoes and potatoes, contain solanine, a toxic alkaloid that can cause severe health issues in horses. Symptoms include trembling, weakness, and gastrointestinal upset. It is vital to keep horses away from any plants within this family.
Garlic and onions contain compounds called N-propyl disulfide and thiosulfates, which can lead to hemolytic anemia if ingested by horses. This condition results in the breakdown of red blood cells, causing weakness and even death.
Rhubarb should not be fed to horses because of its high oxalic acid content which may cause kidney damage and gastrointestinal irritation.
Feeding meat and dairy products is not suitable for horses, as they are herbivores with digestive systems designed for a plant-based diet. Introducing animal-derived products can cause digestive issues and contribute to discomfort, gas, and diarrhea.
Lastly, horses need to avoid the consumption of toxic plants such as oleander, red maple, and bracken fern. These plants can cause various health issues, including cardiac and neurological damage.
By knowing which foods to avoid, horse owners can help maintain their animal’s health and safety. A diet consisting of quality hay, fresh water, and appropriate grains is the key to ensuring optimal equine health.
Treats and Snacks for Horses
Horses enjoy a variety of treats and snacks as rewards or simply to break the monotony of their regular diet. It is important to ensure that the treats provided are safe and appropriate for a horse’s nutritional needs. Some popular treats that horses enjoy include carrots, apples, sugar cubes, and peppermints.
Carrots and apples are natural, healthy options that provide essential vitamins and minerals while satisfying the horse’s craving for something sweet. They should be served in smaller pieces to prevent choking and to allow for easy consumption. It is worth noting that these treats should be given in moderation, as excessive amounts may lead to obesity or digestive issues.
Sugar cubes and peppermints are classic favorites among horse owners. They offer a quick reward and can help create a positive bond between the horse and its handler. However, these treats should be given sparingly as they are high in sugar and may contribute to weight gain or other health problems if consumed in large quantities.
When considering the best horse treats, opting for low-sugar alternatives is a wise choice. Some options include:
- Specially formulated horse treats available at feed stores
- Plain, unsweetened cereals
- Fresh fruits and vegetables, such as celery, banana slices, or squash
Remember, the key to providing treats and snacks for horses is moderation. It is important to maintain a balanced diet with a primary focus on high-quality hay, forage, and feed. Treats should be an occasional extra, not a mainstay in the horse’s daily intake.
Always prioritize the health and well-being of the horse when choosing treats. By carefully selecting appropriate, safe treats and snacks, horse owners can enjoy the bonding experience while supporting the overall health of their equine companions.

Understanding Wild Horse Diets
Wild horses are known to have a diet primarily based on forage. Their natural behavior in the wild consists of spending a large portion of their day grazing on various plant-based foods. By observing wild horses and understanding their diet, one can learn the essentials of their dietary preferences and requirements.
In the wild, horses rely on their continuous grazing habit to consume small amounts of food throughout the day. They mainly feed on grasses and other plant-based foods that are readily available in their habitat. This type of diet allows wild horses to maintain a healthy body condition, providing them with essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals. Some of the plants consumed by wild horses include:
- Grasses
- Legumes
- Herbs
- Shrubs
These plant-based foods can vary in nutritional value, depending on factors such as location, season, and weather conditions. Wild horses are known to adapt to a diverse range of plants, which contributes to their resilience in different environmental conditions.
Understand that wild horses have different dietary needs compared to their domesticated counterparts. In their natural habitat, wild horses have access to a greater variety of forage sources. This variation in diet may contribute to a more balanced intake of nutrients and better resistance to diseases.
The diet of wild horses primarily consists of forage, with their natural behavior involving continuous grazing throughout the day. Their diet mainly comprises grasses, legumes, herbs, and shrubs, which provide essential nutrients for maintaining a healthy body condition. Knowledge of wild horses’ diets can help horse owners make informed decisions about their domestic horses’ dietary needs and promote natural grazing behavior.
Consulting with Equine Nutritionists
Equine nutritionists are professionals who specialize in understanding the dietary requirements and nutritional needs of horses. They work closely with veterinarians to provide tailored advice, ensuring optimal health and performance for each animal.
When seeking guidance, it is crucial to consult with a qualified equine nutritionist or veterinarian who can assess the horse’s specific needs and recommend a suitable diet plan. Some factors to consider when determining a horse’s dietary requirements include age, weight, breed, activity level, and overall health status.
An equine nutritionist can help design a balanced diet by analyzing the nutrients in the horse’s current ration and making recommendations based on its individual needs. They may suggest adjustments to the horse’s diet or recommend nutritional supplements when necessary. The primary components of a horse’s diet are forage, concentrates, and water.
Forage, such as hay and grass, should make up the bulk of the horse’s diet. According to one study, many horse owners underestimate the amount of hay their horses should eat. Ideally, a horse should consume at least 2% of its body weight in forage daily. Concentrates, such as grains or pelleted feeds, can be added to meet additional energy requirements, particularly for horses with higher activity levels or those needing to gain weight.
In addition to providing professional advice on dietary requirements, equine nutritionists and veterinarians can also help diagnose and manage potential nutrition-related issues, such as gastrointestinal problems, dental issues, allergies, or weight management concerns. Regular consultations with a nutrition professional can help prevent health issues from arising, and enable owners to provide the best possible care for their horses.
Consulting with an equine nutritionist or veterinarian is essential for understanding and meeting the individual needs of a horse, ensuring optimal health and performance. By working with these professionals, horse owners can make well-informed decisions about their horse’s diet and welfare.
Frequently Asked Questions
What types of food are included in a horse’s diet?
Horses primarily eat forages, such as hay and grass. They also consume grains like oats, barley, and corn as a source of energy. Concentrate feeds, which are a mix of grains and other ingredients, are often used to supplement their diets. Additionally, horses require access to fresh water at all times.
Which human foods are safe for horses to consume?
Some human foods are safe for horses, like apples and carrots, which make for popular treats. Other safe options include watermelon, bananas, and berries. However, horses should only have these in moderation. It is essential to avoid feeding them toxic foods such as chocolate, avocado, caffeine, and onions.
Are there any specific vegetables that are recommended for horses?
Carrots, beets, and celery are safe vegetables for horses to consume, as they provide additional nutrients to their diet. However, like fruits, these should be given in moderation and not replace essential forages and concentrate feeds.
Is it true that horses are herbivorous and do not eat meat?
Yes, horses are herbivorous and have a digestive system designed to process plant-based diets. Their natural diets primarily consist of grasses and other plant materials. Horses do not eat meat and providing them with a meat-based diet can potentially harm their digestion and overall health.
What is the natural diet of wild horses compared to domesticated breeds?
Wild horses have a diet mainly consisting of grasses, forbs, and shrubs, with limited access to grains. They graze for extended periods throughout the day to meet their nutritional needs. Domesticated horses, on the other hand, often have more limited grazing opportunities. Therefore, they rely on hay and grain-based concentrated feeds, which are specifically formulated to fulfill their nutritional requirements.
How does the nutritional requirement of horses vary with age and activity level?
Young, growing horses have higher protein, mineral, and vitamin requirements than adult horses. Pregnant and nursing mares also need additional nutrients to support fetal growth and milk production. Working horses or those participating in athletic events require increased energy, protein, and mineral intake due to their higher activity levels. It is crucial to consult a veterinarian or equine nutritionist to determine the specific nutritional needs of individual horses.
Sources
- Introduction to Horse Nutrition
- Equine Nutrition and Feeding
- Feed Your Horse Like a Horse: Optimize Your Horse’s Nutrition for a Lifetime of Vibrant Health
- Equine Exercise Physiology
- Survey of Feeding Practices, Supplement Use, and Knowledge of Equine Nutrition Among a Subpopulation of Horse Owners in New England
Last Updated on December 26, 2023 by Nate Dewsbury